MELSEC MX Controller MX-R model
Products -Improving program development efficiency-

Reduce programming time and streamline development with one-tool engineering and intuitive operation
Sequence control and motion control programs are combined into one. There is no need to create separate programs for each module or exchange data, simplifying your programs. With a single tool handling both sequence and motion control programs, you can easily modularize the program into components, manage change history, and debug.
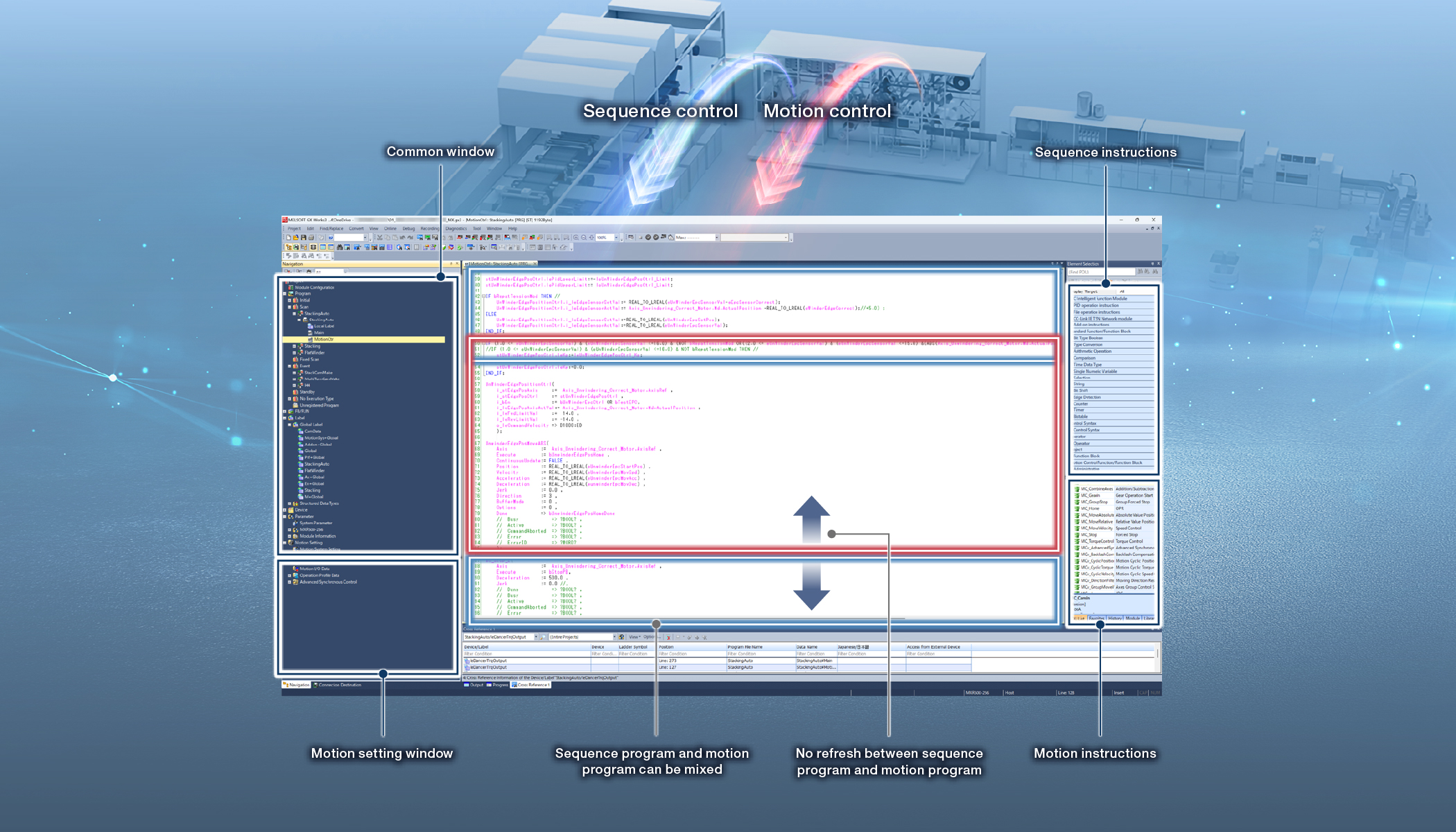
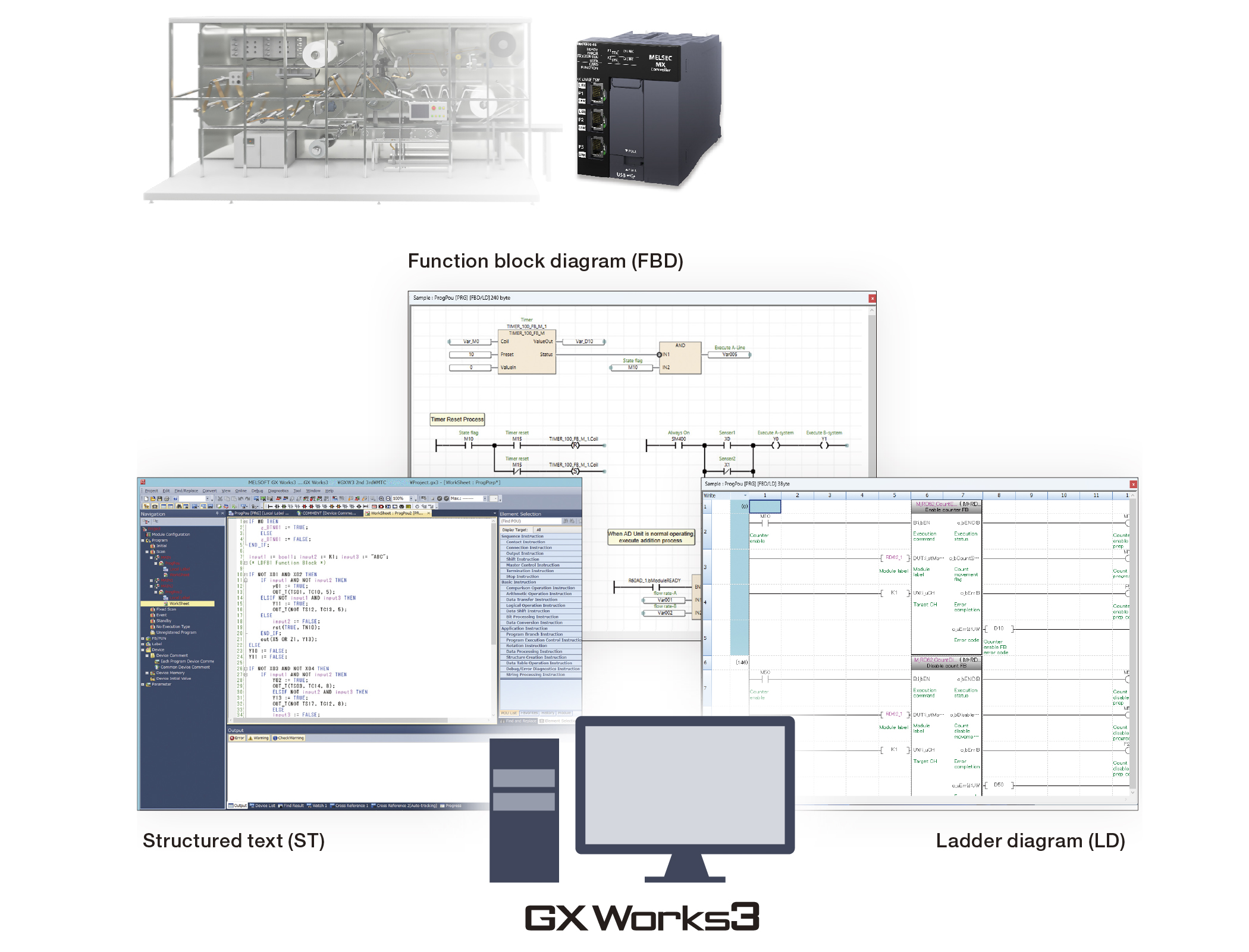
Programming using IEC 61131-3 languages
Ladder diagram (LD), structured text (ST), and function block diagram (FBD) are supported. Motion control programming also supports LD, ST, and FBD, allowing the use of FBs that conform to the international PLCopen® Motion Control FB standard.

The PLCopen®-compliant Motion Control FB interface is standardized,
making it easier for others than the original programmer to understand program content,
reducing design and maintenance time.
Reduce programming effort with labels and structures
Improve program readability by managing signals such as sensor signals with labels named according to their role and use. Using labels allows you to program without worrying about devices used in other programs when creating multiple programs.
What is a label?
A variable that is used by a program, instead of a device. Label names and data types can be defined optionally according to their role and use.
Program readability can be improved by using labels.
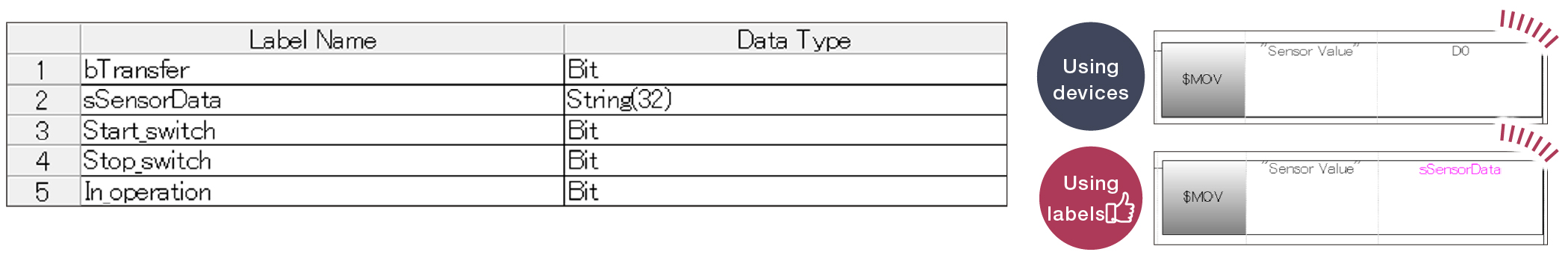
- ■Duplication of addresses used by devices does not need to be considered.
- ■The usage of data can be understood from the specified label name even without a comment.
- ■Changes to a label are reflected in all the same labels, so that working hours can be reduced.
What is a structure?
A structure unifies labels of multiple types (data types) to define a new data type. Using structures helps arrange and manage data and improves reusability.
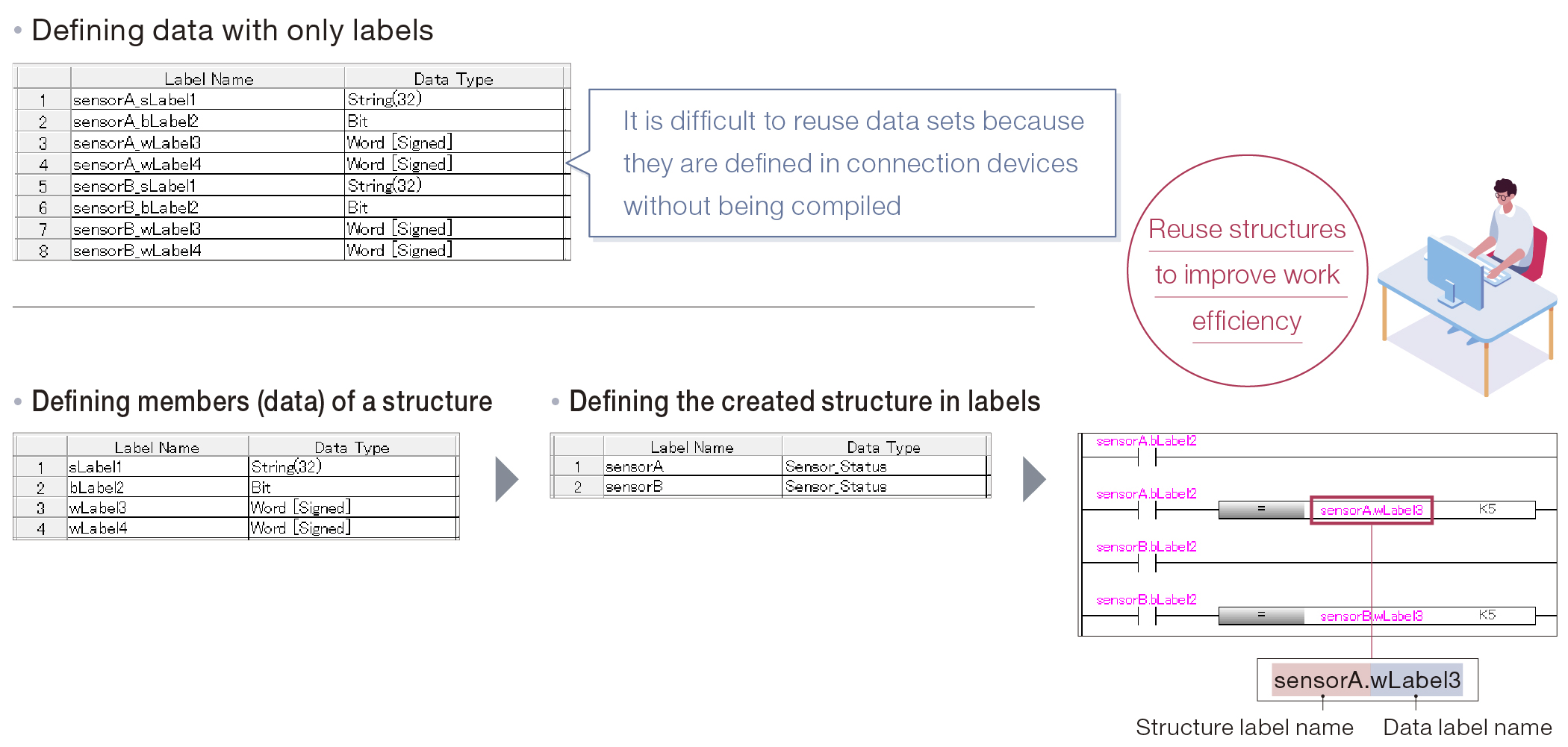
- ■Data structures can be reused among programs that perform similar processing.
- ■Structures can also be reused in programs of other machines.
What is an array?
Data of the same type can be managed by number in an array. You can easily handle large amounts of data by using arrays.
Multiple devices can be used as arrays or structures
The label information (network labels) of devices can be used as bit arrays, structures, and structure arrays, so that programming efficiency can be improved.
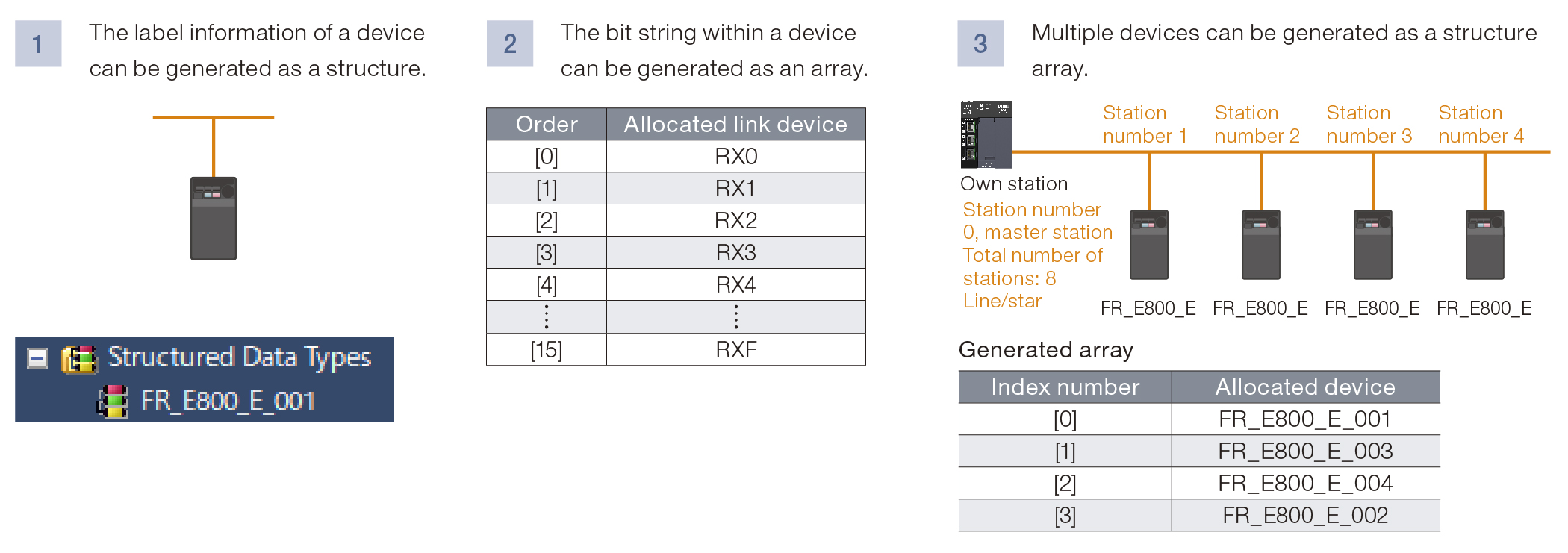
- ■Programming, such as index specification, can be performed by specifying an array element in the structure array.
Supporting arrays
By defining elementary data types, structures, and FB types as an array, the same FB can be declared/described at once. The program can be simplified because there is no need to call the same FB again.
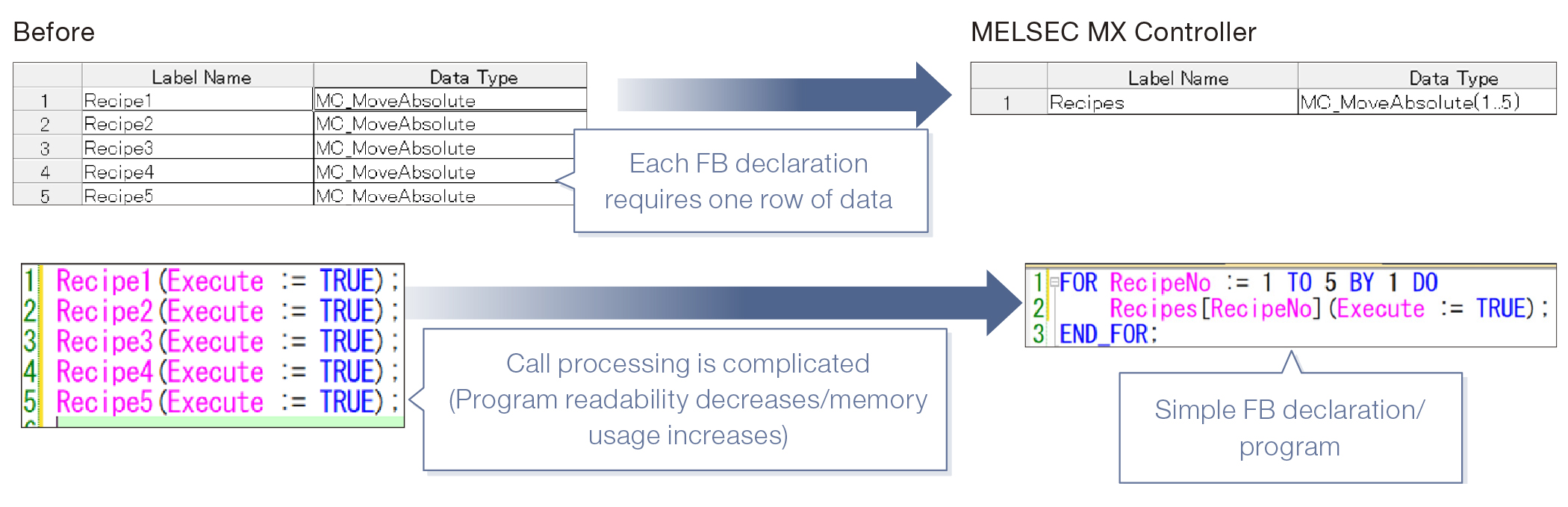
- ■The same FB can be declared/described at once so that programming time can be reduced.
Supporting the label initial value setting in a table format
You can set initial values for array elements and structure instances on the label editor. This eliminates the need for initial value setting programs, reducing the program capacity and the scan time.
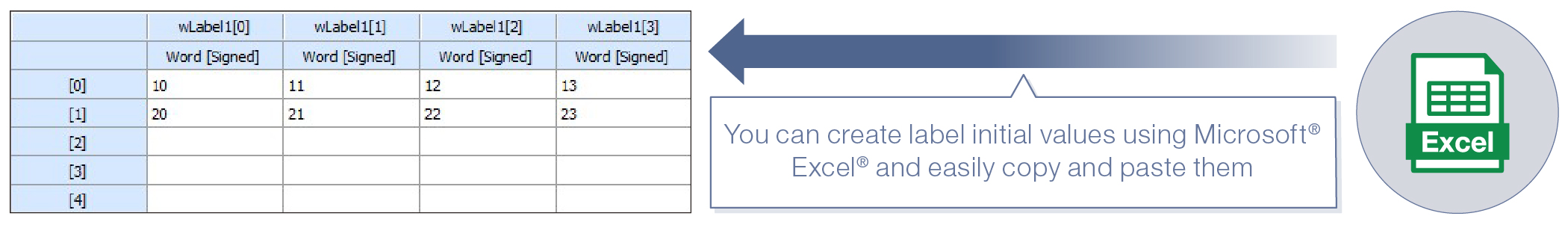
- ■The initial values can be set to array elements, reducing the programming time.
Streamline your project development by modularizing programs into components
Increase program reusability by using label names, FBs, structures, and arrays to modularize a program into components. This approach not only reduces development time but also creates more readable programs. It also ensures consistent programming quality regardless of developer skill level. Each component can be assigned to a specific member, clarifying roles and responsibilities.
Example of combination of labels, FBs, and structures
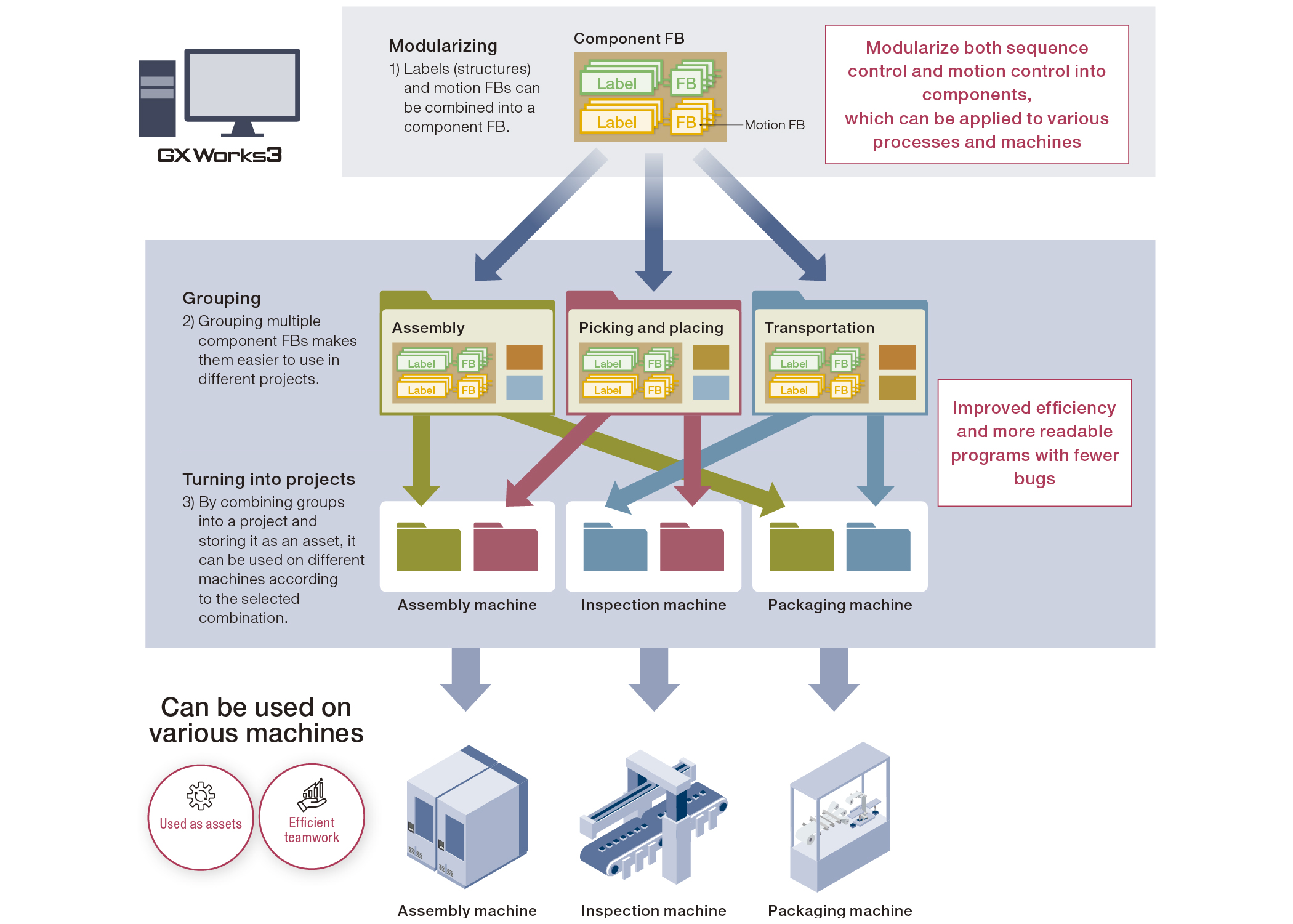
Efficiently develop large-scale projects with multiple members using program configuration management
Program configuration management enables program reuse and collaboration.
Changes made by others are reflected immediately, with centralized history management for easy tracking of changes.
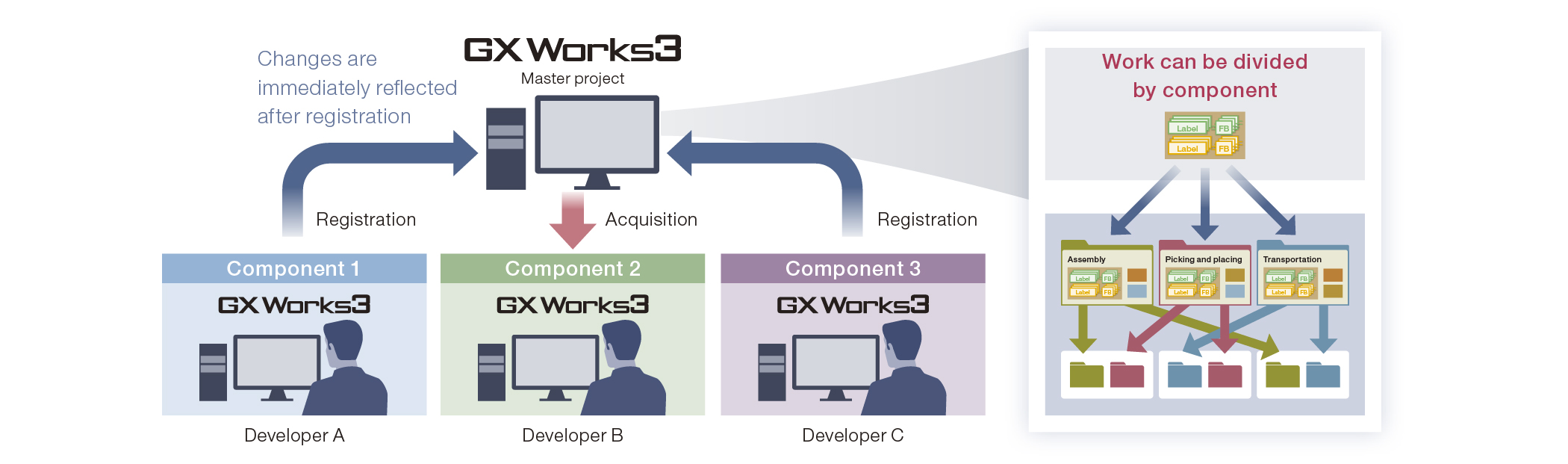
Program history log can be kept
You can track which version caused a machine failure.
●Data registration method
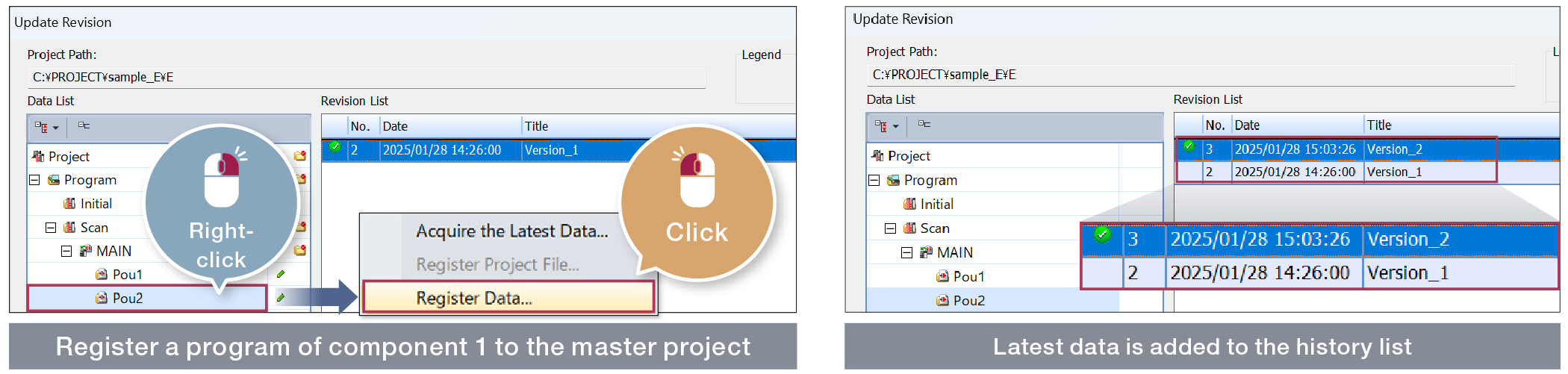
- You can track who changed which components and when.
- Edited data is not overwritten by others.
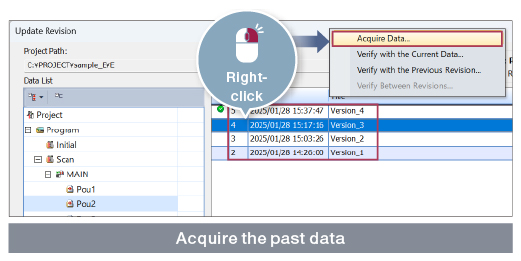
Data can be restored for only a specific part
Sudden machine failures can be responded to quickly.
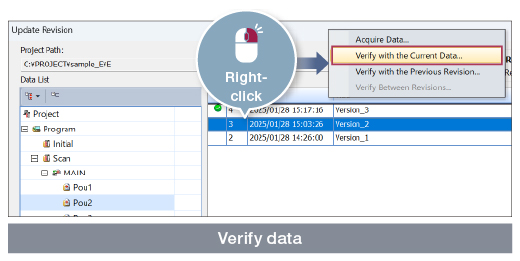
●Verification method
●Rollback method
Reduce commissioning time for multi-axis machines
Easy axis generation
Real drive axes can be generated from network configuration information. Generating axes based on network configuration settings reduces the time and effort required to set up axes.
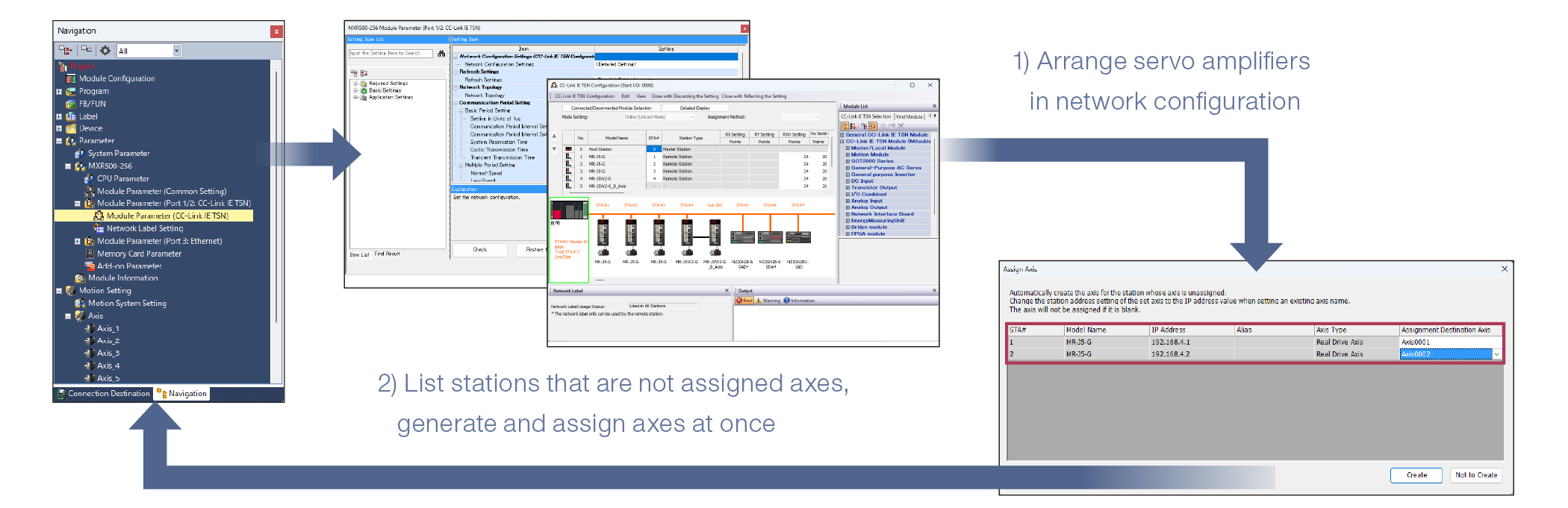
- ■Axes can be generated at once for servo amplifiers that are not assigned axes.
Setting IP addresses of axes at once
You can view a list of stations assigned to each axis and change their IP addresses.
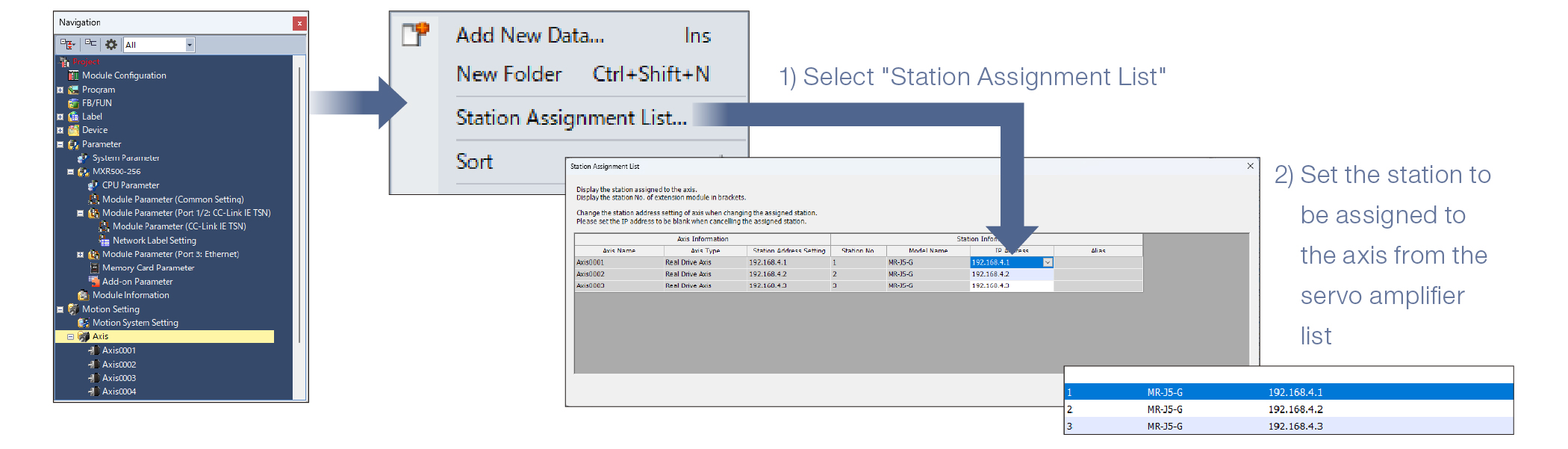
- ■The IP address of the station to be assigned to the axis can be set at once.
Easy multi-axis positioning settings
You can set multi-axis positioning data (point table) from a dedicated window. Continuous positioning can be performed with one FB.
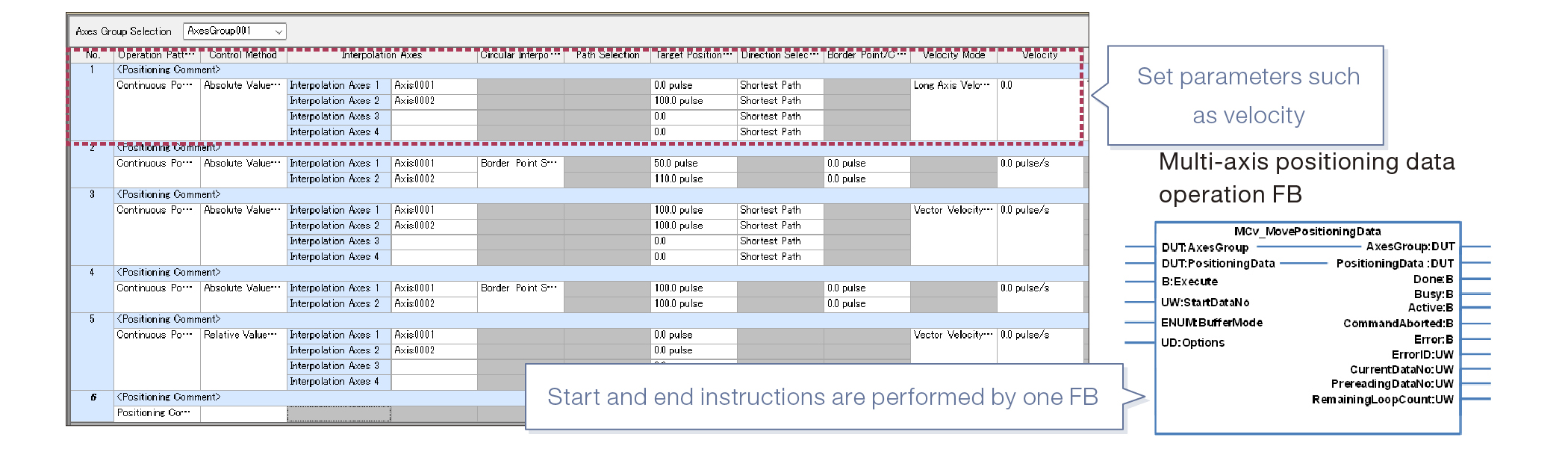
- ■The FB with multi-axis control is supported.
- ■FB control data can be set collectively on the dedicated window.
- ■By creating multiple operating patterns, continuous positional control can be implemented with one FB.